Rotary Encoders
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Explanation of Terms | Troubleshooting |
Resolution
The pulse count of an incremental signal output when the shaft revolves once, or the absolute address count.
The output signal count for an Incremental Encoder. There are 1- phase models (phase A), 2-phase models (phase A, phase B), and 3- phase models (phase A, phase B, and phase Z). The phase Z is an origin signal that is output once a revolution.
Output Phase Difference
When the shaft is rotated, this is the time difference between the rise or fall of the phase A and phase B signals, expressed as a proportion of the period of one signal, or as an electrical angle where one signal period equals 360°.
The difference between phase A and phase B as an electrical angle is normally 90°.
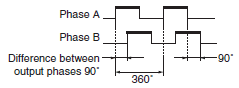
CW
The clockwise direction of rotation. Viewed from the end of the shaft, the shaft rotates clockwise. With an Incremental Encoder, phase A normally leads phase B in this rotation direction. With an Absolute Encoder, this is the direction of code increase.
The reverse of CW rotation is counterclockwise (CCW) rotation.
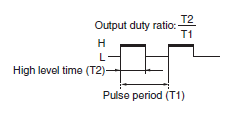
This is the ratio of the duration of high level during one period to the average period of pulse output when the shaft is rotated at a constant speed.
The maximum frequency at which the signal can respond.
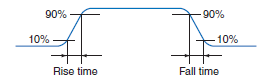
Rise and Fall Times of Output
The elapsed time from a 10% to 90% change in the output pulse.
1.Open-collector Output
An output circuit where the emitter of the output circuit transistor is the common and the collector is open.
2.Voltage Output
An output circuit where the emitter of the output circuit transistor is the common and a resistor is inserted between the collector and the power supply to convert the output from the collector to a voltage.
3.Line-driver Output
An output method that uses a special IC for high-speed, long-distance data transmission that complies with the RS-422A standard. The signal is output as a differential secondary signal, and thus is strong with respect to noise.
A special IC called a line receiver is used to receive the signal output from a line driver.
4.Complementary Output
An output circuit with two output transistors (NPN and PNP) on the output.
These two output transistors alternately turn ON and OFF depending on the high or low output signal. When using them, pull up to the positive power supply voltage level or pull down to 0 V. The Complementary Output allows flow-in or flow-out of the output current and thus the rising and falling speeds of signals are fast. This allows a long cable distance.
They can be connected to open-collector input devices (NPN, PNP).
The torque needed to rotate the shaft of the Rotary Encoder at startup.
The torque during normal rotation is normally lower than the starting torque. A shaft that has a waterproof seal has a higher starting torque.
Moment of Inertia
This expresses the magnitude of inertia when starting and stopping the Rotary Encoder.
Shaft Capacity
This is the load that can be applied to the shaft. The radial load is the load that is perpendicular to the shaft, and the thrust load is the load in the direction along the shaft. Both are permitted on the shaft during rotation, and the size of the load affects the life of the bearings.
Ambient Operating Temperature
The ambient temperature that meets the specifications, consisting of the permitted values for the external air temperature and the temperature of the parts that contact the Rotary Encoder.
Ambient Storage Temperature
The ambient temperature when the power is OFF that does not cause functional deterioration, consisting of the permitted values for the external air temperature and the temperature of the parts that contact the Rotary Encoder.
Degree of Protection
The level of protection against penetration of foreign objects from outside the Rotary Encoder. This is defined in the IEC60529 standard and expressed as IPXX.
The degree of protection against oil is specified by OMRON standards, and is expressed as oil-proof construction or oil resistance.
Absolute Code
(1)Binary Code
A pure binary code, expressed in the format 2n. Multiple bits may change when an address changes.
(2)Gray Code
A code in which only one bit changes when an address changes. The code plate of the Rotary Encoder uses Gray Code.
(3)Remainder Gray Code
This code is used when expressing resolutions with Gray Code that are not 2n, such as 36, 360, and 720. The nature of Gray Code is such that when the most significant bit of the code changes from 0 to 1 and the same size of area is used for both the larger value and the smaller value of objects, the signal only changes by 1 bit within this range when changing from the end to the beginning of a code.
This enables any resolution that is an even number to be set with Gray Code. In this case, the code does not begin from 0, but from an intermediate code, and thus when actually using a code it must first be shifted so that it starts from 0.
The example in the code table shows 36 divisions. For the change from address 31 to 32, the code extends from address 14 to 49 when 18 addresses each are taken for the objects. When changing from address 49 to 14, only one bit changes, and we can see that the characteristic of Gray Code is preserved. By shifting the code 14 addresses, it can be converted to a code that starts from address 0.
(4)BCD
Binary Coded Decimal Code.
Each digit of a decimal number is expressed using a binary value.
In contrast to parallel transmission where multiple bits of data are simultaneously output, this method outputs data serially on a single transmission line, enabling the use of fewer wires.
The receiving device converts the signals into parallel signals.
Hollow Shaft
The rotating shaft is hollow, and the drive shaft can be directly connected to the hole in the hollow shaft to reduce the length along the direction of the shaft. A leaf spring is used as a buffer to absorb vibration from the drive shaft.
The rotating slit disk in the Encoder is made of metal for higher shock tolerance than glass. Due to slit machining limitations, the metal disk cannot be used for high-resolution applications.
A method of mounting the Encoder in which a Servo Mounting Bracket is used to clamp down the flange of the Encoder. The position of the Encoder in the direction of rotation can be adjusted, and thus this method is used to temporarily mount the Encoder to adjust the origin.
Absolute Code Table
| Decimal | Binary | Gray | Gray remainder 14 | BCD | |
| 10 | 1 | ||||
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 | 0 0 0 1 0 2 0 3 0 4 0 5 0 6 0 7 0 8 0 9 1 0 1 1 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 6 1 7 1 8 1 9 2 0 2 1 2 2 2 3 2 4 2 5 2 6 2 7 2 8 2 9 3 0 3 1 3 2 3 3 3 4 3 5 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 |