Photomicro Sensors
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Explanation of Terms | Troubleshooting |
| Term | Reference diagram | Explanation | |
| Non-modulated light Modulated light | 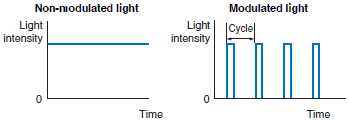 | Non-modulated light: Method used to detect light steadily emitted by the emitter element. Modulated light: Method used to detect light emitted in pulses by the emitter element. | |
| Sensing distance | Through-beam Sensors (with slot) | 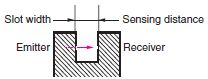 | The slot width, i.e., the distance between the opposing faces of the emitter and receiver, is the sensing distance. |
| Through-beam Sensors |  | The minimum distance that can be set considering factors such as the variation between products and fluctuations in temperature. Note: The actual value under standard conditions for each method is longer than the rated sensing distance. | |
| Retroreflective Sensors | 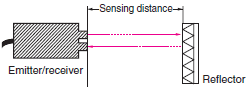 | ||
| Diffusereflective Sensors Limitedreflective Sensors | 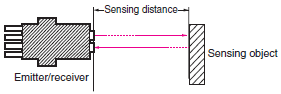 | The minimum distance that can be set for a standard sensing object (white paper) considering factors such as the variation between products and fluctuations in temperature. Note: The actual value under standard conditions for each method is longer than the rated sensing distance. | |
| Differential distance | 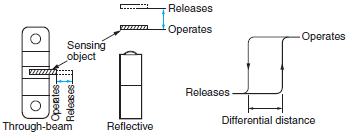 | The difference in distance between the operating point and releasing point. | |
| Response frequency | 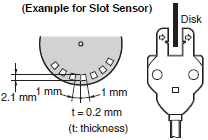 | The frequency at which an object satisfying specified conditions (size, transparency rate, reflection factor, sensing distance, and power supply voltage) can be repeatedly detected. | |
| Response time | 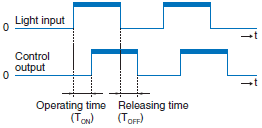 | The delay from the light input turning ON/OFF until the control output operation or release operation. The following equation generally applies. Operating time (Ton) ≈ Releasing time (Toff) | |
| Ambient illumination | 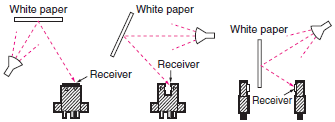 | The level of illumination on the sensing surface that enables stable operation of the Sensor. | |