Outline of Major Standards
International Standards
International standards consist of the IEC standards related to electricity and the ISO standards related to other areas (e.g., machines and management.)
IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission)
The IEC is a standardization commission founded in 1906 to promote unification and coordination of international standards relating to electricity. It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland.
Based on reports from member nations on the latest science technologies in those nations, IEC standards are issued as technological standards relating to electricity. Established international safety standards provided by various countries and accepted worldwide are based on IEC standards.
The IEC standards committees includes the CISPR (International Special Committee on Radio Interference) that makes standards for EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility).
To simplify certification procedures for electrical devices and promote smooth international trade, there is an international scheme called CB Scheme (Certification Body Scheme), which is authorized by IEC standards. Based on the CB Scheme, safety tests on electrical devices are conducted and certificates are issued if the devices are proved to meet IEC standards.
ISO (International Organization for Standardization)
ISO is a standardization organization that started official activities in 1947 to promote international standards in all areas (e.g., machines and management) except for electricity, which is covered by the IEC, by issuing ISO standards. It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland.
North America
UL Standards (Underwriters Laboratories Limited Liability Company)
![]()
In 1894, UL was established as the Underwriters' Electrical Bureau. UL conducts testing, evaluation, and certification for UL standards and other standards. UL is accredited by the U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) as a Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory (NRTL). And UL certification is generally not a legal requirement, but it is highly regarded in many states and cities in the U.S. as a reliable indicator of product safety. To obtain UL certification, it is common practice to obtain UL certification not only for the product itself, but also for the main parts.
Our company handles two types of certified products: Component Recognition and Listing. Component Recognition refers to certification for parts intended to be incorporated into equipment. Products certified with Component Recognition are marked with the Recognized Component Mark (left). The certification includes specified conditions of use. Displaying the Recognized Component Mark may be optional in some cases.

Listing generally refers to certification for end products and complete components. Products with Listing certification are marked with the Enhanced UL Mark (top left) or the Listing Mark (middle left).
The Enhanced UL Mark consists of the UL Basic Certification Mark and a description such as file number. The country code appears above the file number.
For more details, please refer to UL's Marks and Label Hub.
(https://markshub.ul.com/information-and-requirements)
Note: The file numbers and country codes appearing in the Enhanced UL Mark are examples. The numbers and codes contained vary from product to product.
UL is authorized to issue certification for compliance with Canadian standards.
In the case of conformity to Canadian standards, each country code of the Enhanced Mark, Listing Mark and Component Mark have a symbol indicating that the product is intended for Canada.

The mark on the UL Badge (bottom left) can be used for promotional purposes on catalogs, instruction manuals, packaging boxes, etc., for products that display the Enhanced UL Mark.
CSA (CSA Group)

Established in 1919 as a non-profit, non-governmental standardization organization (Canadian Standards Association). The CSA Group develops standards, conducts testing, and performs inspections and certifications.
Products and components certified by the CSA Group display the mark. The CSA Group is recognized by the U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) as a Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory (NRTL). This certification allows products to be marked to indicate that they comply with both Canadian and US standards.
Oceania
RCM (Regulatory Compliance Mark)
![]()
This is a mandatory mark to show compliance with electrical safety, EMC, radiocommunications, and telecom requirements for products that are distributed to Australia or New Zealand.
Under the previous system, there were individual marks, such as the C-Tick mark for EMC and A-Tick mark for telecom, but these were unified to the RCM mark on March 1, 2013. A transition period until February 28, 2016 was established that permitted the marks for the previous system for some products, but displaying the RCM is now required of all products.
For the devices in scope of RCM, steps such as certification, product registration, declaration of conformity are taken and the RCM is required to be displayed on the product according to requirements.
Europe
EN (European Norm) Standards
Of the EN standards related to electricity, standards beginning with "EN6" are based on IEC standards and those beginning with "EN55" are based on IEC-CISPR standards. Standards beginning with "EN5" are unique EU standards that do not exist in the IEC standards.
EU (European Union) Directives
![]()
In the EU (European Union), EU Directives are announced to instruct the creation of laws in the EU member countries. A product can display the CE Mark only when it conforms to all of the directives applicable to it, such as the New Approach Directives, which cover the Machinery Directive, Low Voltage Directive, and the EMC Directive. As a rule, EN standards announced as Harmonized Standards in the Official Journal of the European Union are used to evaluate compliance with the Directives.
UKCA (United Kingdom Conformity Assessed)

As the UK exited the EU, this is a compulsory rules came into effect on January 1, 2021, to replace the EU CE mark as a mark of conformity to show compliance with applicable UK laws and regulations. Immediately after exiting from the EU, the products covered, technical requirements, conformity assessment process, and standards are almost same to the CE mark based on the European Union (Withdrawal) Act 2018.
The start of the obligation to display the UKCA mark, which was originally scheduled for January 1, 2022, has been postponed, and as of September 2024, the UK government intends to extend recognition of the CE marking for 21 regulations placing on the market in Great Britain, indefinitely, beyond 31 December 2024, allowing businesses will have the flexibility to use either the UKCA (UK Conformity Assessed) or CE marking to sell products in Great Britain.
EAC (Eurasian Conformity)
![]()
As for products distributed in the region of Eurasian Economic Union (Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Armenia and Kirghiz), it is required to comply with the requirements of technical regulations such as electric safety and EMC.
EAC came into effect on February 15, 2013 as a regulation for products distributed in the Customs Union region of Russia, Belarus and Kazakhstan and it has been the mandatory regulation since March 15, 2015. However, after Eurasian Economic Union was launched on January 1, 2015, EAC was taken over by Eurasian Economic Union.
According to the requirements of the technical regulations, obtaining of the certification or declaration of the conformity is required. EAC marking for the products is also required.
China
CCC (China Compulsory Certification) Mark

As a result of China joining the WTO (World Trade Organization) in 2001, the previous Safety License System for Import Commodities and the Compulsory Supervision System for Product Safety Certification were combined to form the CCC. The change was announced on 3 December 2001 and implemented from 1 May 2002. Starting 1 August 2003, any products that have not received the CCC Mark are prohibited from import to or sale in China.
Products Subject to CCC Mark: 16 product sections consisting of 104 product categories as of September 13, 2024
Applicable Standards: National Standards (GB: Guojia Biaozhun) (Standards related to electricity were based on IEC standards.)
CCC Mark: Display of the CCC Mark is legally required.
Korea
S Mark
![]()
Korea S-mark is a voluntary certification system established by the Korea Occupational Safety and Health Authority (KOSHA) in November 1997 for the purpose of reducing industrial accidents.
Based on the Korean Occupational Safety and Health Act, the Korea Occupational Safety and Health Authority (KOSHA) conducts a comprehensive review of the safety and reliability of products used in the industrial field, as well as the quality control capabilities of manufacturers. This is a certification mark issued to products that have been determined, that the standards are met, and products that have been certified are required to display the S-mark.
KC Mark

KC Mark is an abbreviation of Korea Certification Mark, which is a compulsory certification mark in Korea. There are multiple certifications that apply the KC Mark, one of which is the EMC regulations under the Korean Radio Waves Act, which also covers industrial equipments. Targeted devices are required to obtain Self-Conformity Verification, Conformity Registration or Conformity Certification from the Radio Research Agency (RRA), and products that have been certified are required to display the KC Mark.
KCs Mark

This is a mandatory regulation controlled by Korea Occupational Safety and Health Agency (KOSHA) and is based on the Korean Occupational Safety and Health Act. The conformity mark is KC with an “s” indicating the safety field (KCs mark). Safety Certification is required for hazardous or dangerous machinery, etc., prescribed by Presidential Decree as potentially causing risk to the safety and health of employees. If the hazardous or dangerous machinery, etc. prescribed by Presidential Decree, other than machinery, etc. subject to Safety Certification is required Autonomic Safety Verification. Safety Certification and Autonomic Safety Verification also include apparatus, equipment, and protective devices and protectors.
India
BIS (CRS) Mark
Compulsory Registration Scheme (CRS) established by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS). For regulated items, compliance with standards, license registration, mark display, etc. are required. When the Scheme started at 2013, the target items were mainly consumer goods, but the scope of target items has been gradually expanding, and some industrial equipment has now also been included in the target items.
Shipping Standards
There are more than 20 classification societies worldwide that individually work to create regulations and certify compliance. The IACS (International Association of Classification Societies) works as an international body currently consisting of 10 member classification societies plus 2 associate classification societies. The IACS (International Association of Classification Societies) works as an international body and currently consisting of 12 member classification societies. The classification societies in the IACS certify and register 90% of the world's ships.
Classification certification has a close relationship to maritime insurance. Insurance underwriters will as a rule insure only ships that have been classified and refuse those without a certified classification. Therefore, automation devices used on ships must conform to classification standards of individual countries if so requested by the owner.
Regulation (EC) No. 391/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 April 2009 on Common Rules and Standards for Ship Inspection and Survey Organizations Article 10, which went into effect in June 2009, requires the mutual recognition of certificates for maritime items issued by EU regulatory organizations (ROs).
As a result, from 2013, the mutual recognition between the eleven EU RO member classification societies is being implemented in stages. Applicants can select whether to apply for mutual recognition or individual recognition.
However, mutually recognized certificates that are issued by other EU ROs are not valid for Japanese ships and mutual recognition is not implemented.
Note: The EU ROs consist of the following 11 certification bodies that are approved by the EU: ABS, BV, CCS, CRS, DNV, IRS, KR, LR, NK, RINA, PRS.
IACS Member Classification Societies
- ABS: American Bureau of Shipping
- BV: Bureau Veritas (France's classification society)
- CCS: China Classification Society
- CRS: Croatian Register of Shipping
- DNV: Det Norske Veritas (Norway's classification society)
- IRS: Indian Register of Shipping
- KR: Korean Register of Shipping
- LR: Lloyd's Register of Shipping (Britain's classification society)
- NK: Nippon Kaiji Kyokai (Japan's classification society)
- PRS: Polish Register of Shipping
- RINA: Registro Italiano Navale (Italy's classification society)
- Türk Loydu (Turkey’s classification society)
Other Classification Societies
- CR: China Corporation Register of Shipping (Taiwan's classification society)
Japan
Electrical Appliance and Material Safety Act
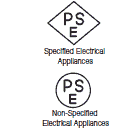
The Act is to aim preventing hazards and electromagnetic interference by means of regulating the manufacture, sale, etc. of Electrical Appliances and Materials.
The Act specifies about 457 items of the Electrical Appliances and Materials as of 2023-10-01.
As Specified Electrical Appliances and Materials are 116 items, those which are particularly likely to cause hazards because of their structures, methods of use, or other conditions, including (i) those used for long hours with no supervision, (ii) those used by the socially vulnerable, and (iii) those used in direct contact with the human body, have been designated.
Non-Specified Electrical Appliances and Materials are 341 items resulting from deducting the 116 Specified Electrical Appliances and Materials.
Article 2 of the Ordinance Concerning Technical Requirements for Electrical Appliances and Materials specifies technical requirements harmonized with IEC standards on April 1, 2002.
Other major safety certifications
Certification marks from certification bodies are displayed as indication of product safety certification.
The most common marks are as follows.
![]()
- VDE (Verband Deutscher Electroechnischer e.V.)
![]()
- TÜV Rheinland (Technischer Überwachungs Verein Rheinland e.V.)
![]()
- TÜV SÜD (Technischer Überwachungs Verein SÜD e.V.)